Disaster management is the discipline dealing of with and avoiding risks. It is a discipline that involves preparing, supporting, and rebuilding society when natural or human-made disasters occur. In general, any Disaster management is the continuous process by which all individuals, groups, and communities manage hazards in an effort to avoid or ameliorate the impact of disasters resulting from the hazards. Actions taken depend in part on perceptions of risk of those exposed
Disaster Management cycle
The traditional approach to disaster management has been to regard it as a number of phased sequences of action or a continuum. These can be represented as a cycle..
Recovery
• National, Provincial/LA and District/Division level units of service providing agencies will take immediate action to revive the affected public utilities to provide essential services in affected areas. LAs will immediately attend to all services within their purview. Where services are affected severely, action will be taken to take temporary measures for providing such services immediately.
• In respect of speedy recovery of the disrupted livelihoods of the affected communities, maximum possible assistance will be provided to them, in coordination with government agencies and NGOs, adhering to social justice, neutrality, impartiality, values and culture of affected persons.
• There will be the major agencies responsible for various infrastructure and essential services, which will be associated with these activities and these activities will be coordinated by the DMC at national level and PC, District and Divisional administration..
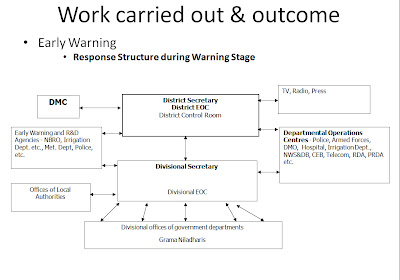
Emergency Operations in case of disaster
· Establishment of District Emergency Operation Centre
· Carrying out Emergency Operations, coordinating with armed forces, police and other related agencies at all levels.
Preparedness Planning (District, Division,Grama Niladhari, School and Hospital level)
· Facilitating, issuing guidelines, coordinating, directing and monitoring of preparedness of disaster preparedness and responses plans at district, divisions and village levels
· Preparedness for timely and effective response, equitable relief distribution, speedy recovery, timely rehabilitation and reconstruction..
• Training, Education & Public Awareness
– Training – Disaster risk reduction related training at all level
– Public awareness – Programmes for officials at levels, school children and community level.
• Disaster Management Technology, Long-term Mitigation & DRR
– Hazard Mapping and Risk Assessment
– Information and Data Collection
– Long term disaster risk reduction
Involvement of Different Stakeholders
Some major stakeholder agencies responsible for (or could be entrusted with) different activities in post disaster recovery, rehabilitation & reconstruction
Expecting Research Areas
• Research studies on disaster related subjects to strengthen the data base on disaster information and assist in the disaster risk assessment studies in prone areas and social issues by R&D agencies and universities will be promoted. Specific studies will be undertaken on technological and human induced hazards; building fire risk; earthquake risk etc.
• To promote research studies on technical as well as sociological aspects on Disaster Management.
• With the integration of DRM in university education, Ph.D., Masters and Bachelor Degree students are now encouraged to select Disaster Risk Management related themes for dissertations. This has been evident from the inquiries made by university students for DRM related materials and information.
• Find the reliable techniques to integrate the DRM in the regular development plan.
• Find the techniques to get the maximum support to utilize the community in the CBDM programme in sociological aspect.
• Which is the best techniques in livelihood based on the climatic change.
• Find the best crops varieties for sustainable development in the extreme condition in flood and drought.





No comments:
Post a Comment